Star anise (Illicium verum) is more than just a decorative spice: its distinctive star shape and unmistakable aroma make it a key ingredient in the world of infusions, tea blends, and spices.
Originating in Asia, it combines tradition and sophistication, offering professionals in the sector new opportunities to innovate in products and presentations.
With each fruit and each seed comes a wide range of possibilities for creating aromatic blends, ground spices, extracts, and other formats that make a difference in the professional world. Exploring this spice means discovering how a singular ingredient can bring identity, versatility, and distinction to any product line within the infusion’s industry.
What is star anise?
Star anise, also known as star aniseed or star anise spice, is the fruit of the evergreen tree Illicium verum, native to Asia and belonging to the Schisandraceae family.
Its star shape, generally with six to eight points, has made it a visual icon in the world of spices. Each point contains a shiny seed, which is used together with the dried pod, adding aroma and distinctive character to tea blends and infusions.
Botanical characteristics
The star anise tree can grow up to 18 metres tall and thrives in tropical and subtropical climates. Its leaves are glossy and lanceolate, while its flowers, in yellowish-green tones, give rise to the characteristic star-shaped fruit.
For businesses dedicated to infusions and spices, these characteristics are highly relevant, as they determine key aspects such as quality standardisation, harvesting at the optimal stage, and the potential for transformation into different commercial formats.
Origin and history of star anise
With roots in southern China and Vietnam, Illicium verum has been present for centuries in Asian culture, especially in gastronomy and in the preparation of hot beverages.
Its expansion to India, the Middle East, and later Europe began in the 16th century, during the era of the great trade routes, when demand for exotic spices was growing across the West. It quickly found its place in sweet recipes, liqueurs, and condiments, establishing itself as a highly valued ingredient.
Today, China remains the world’s main production centre, particularly the provinces of Guangxi and Yunnan, which account for more than 80% of global supply.
Vietnam, India, and other Southeast Asian countries also cultivate it, though on a smaller scale. Beyond its role in the food sector, star anise also holds a significant place in the ingredients and extracts industry, where it is used, among other applications, as a source of shikimic acid—a compound of great interest to the pharmaceutical industry.
Phytochemical composition, active compounds, and flavour
Star anise possesses a complex phytochemical composition that defines its aroma and flavour, elements highly valued in teas, infusions, and spice blends.
Among its main compounds are:
- Anethole: the major component of its essential oils, responsible for the characteristic sweet, aniseed aroma.
- Flavonoids (quercetin, kaempferol): add aromatic complexity and depth of flavour.
- Essential oils (linalool, limonene): provide complementary aromatic notes.
- Tannins and polyphenols: contribute subtlety to aroma and sensory perception.
- Shikimic acid: present in the seeds and pods, known for its importance as a raw material in the ingredients and extracts industry.
The presence of these compounds allows star anise to adapt to different formats (whole fruit, powder, or extracts), offering opportunities to highlight various aromatic and sensory nuances depending on the preparation or blend.
The flavour of star anise
This ingredient, considered a medicinal plant, is distinguished by an intense, sweet flavour with notes reminiscent of liquorice, though deeper and slightly spiced. This complexity makes it a versatile ingredient, ideal for enhancing tea blends, infusions, and aromatic preparations.
Its organoleptic profile can be summarised in three aspects:
- Aroma: sweet, warm, and intense, with liquorice notes perceptible from the first contact.
- Flavour: aniseed, slightly spicy, and persistent, adding character to blends.
- Pairings: naturally combines with spices such as cinnamon, clove, cardamom, fennel, or coriander, enhancing harmony in spiced infusions and chai tea blends.
In star anise infusions, this ingredient releases a rounded and balanced profile, integrating easily with black teas, green teas, rooibos, or herbal infusions, lending a distinctive character without overpowering the blend.
Its sensory presence makes it a highly valued resource for professionals looking to differentiate their products and offer unique aromatic experiences to their customers.
Traditional uses and current applications of star anise
Historically, star anise has been a central ingredient in Asian cuisine, both in savoury and sweet preparations, forming part of iconic blends such as Chinese five-spice.
It was also an important element of traditional Chinese medicine, highly valued as a medicinal plant for its digestive, carminative, and antiviral properties. It was commonly used in hot infusions to relieve colds, digestive issues, and general ailments.
This cultural legacy has established star anise as one of Asia’s most valuable medicinal spices, whose significance has transcended borders and eras, becoming integrated into the culinary traditions of India, the Middle East, and Europe.
Current applications
Today, this spice has expanded its uses and become a global ingredient. Its most frequent applications include:

Star anise infusions
This iconic ingredient brings a sweet, warm, and enveloping profile, with liquorice notes and a spiced touch to teas and infusions. It is especially popular in winter blends, as it not only enhances flavour but also provides digestive and comforting properties.
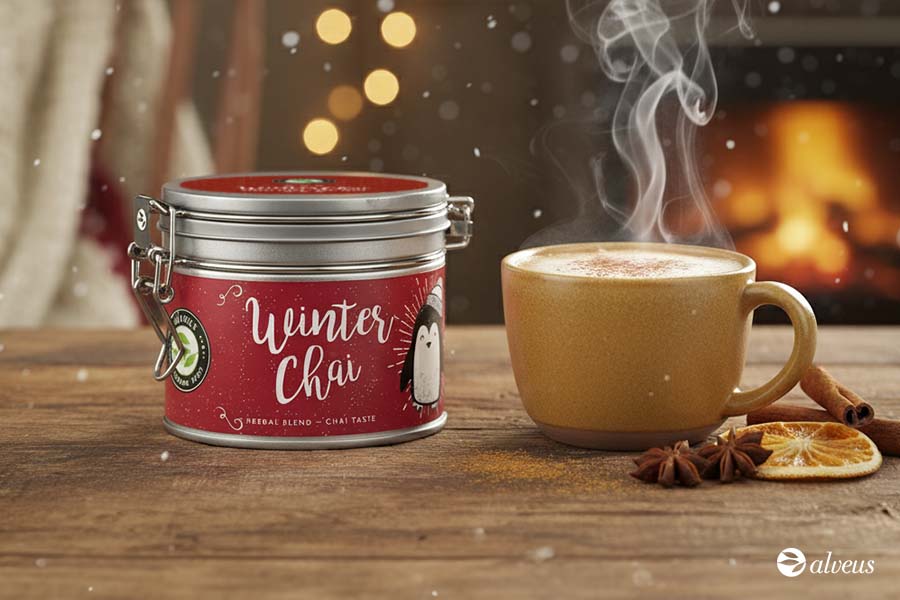

* Winter Chai BIO, organic star anise infusion available for wholesale purchase in our Alveus B2B Shop.
During the Christmas season, star anise infusions become the highlight of preparations such as Christmas chai tea or mulled wine, evoking festive aromas that connect with tradition.
Cosmetics and aromatic products
Its essential oils and concentrated extracts are very common in the production of perfumes, soaps, and candles, where they provide a sweet and spiced aroma.
Pharmaceutical industry
A large share of the harvest is destined for the extraction of shikimic acid, an essential precursor in the synthesis of antivirals, which influences the availability and market price of the spice.
Alcoholic and non-alcoholic beverages
Used in liqueurs, cocktails, and spiced hot drinks to impart distinctive aniseed notes.

Bakery and confectionery
As an aromatic ingredient, it enhances sweets, biscuits, and doughs, bringing an aniseed character often associated with traditional and seasonal recipes.
Formats and uses of star anise
One of the competitive advantages of star anise is the diversity of formats in which it is marketed, allowing it to be adapted to different production needs:
- Whole fruit: valued for its visual appeal in infusions, mixology, and culinary decoration.
- Ground: practical for spice blends, bakery, confectionery, and powdered teas.
- Essential oil: used in the food, cosmetics, and fragrance industries to deliver concentrated flavour and aroma.
- Extracts and oleoresins: standardised formats suitable for applications in beverages, supplements, and high-value-added products.
This variety offers flexibility both to small tea and infusion brands and to industrial manufacturers requiring consistency and uniformity in production.

Production and current market of Illicium verum
International demand for Illicium verum has grown steadily, driven by its culinary value and its use as a raw material in infusions and aromatic beverages.
In today’s market, star anise is positioned as a strategic ingredient for tea and infusion brands, spice businesses, beverage manufacturers, and the pharmaceutical industry. Recognised as a medicinal plant, it maintains a strong and growing demand, particularly driven by:
- The rise of functional infusions and blends.
- Interest in natural, Asian-origin ingredients.
- It has strategic value in the pharmaceutical industry.
However, dependence on a limited number of producing regions presents challenges related to supply security and price stability. For businesses, this makes star anise an ingredient with great potential, but also one that requires careful supply chain management.
An iconic medicinal spice with market potential
The spice market is transforming, driven by consumers who demand authentic, high-quality products with cultural heritage. In this context, star anise emerges as an ingredient that meets all these criteria, allowing companies to position themselves with a versatile and recognisable product.
Beyond its sensory profile, this Asian ingredient stands out for the diversity of its applications and formats. This makes it a resource adaptable to different business models: from small specialised brands seeking visual impact and character in their infusions, to large industries requiring consistency and standardisation in their processes.
Looking ahead, its relevance will only continue to grow. The combination of tradition, identity, and adaptability places it at the heart of opportunities shaping the tea, infusion, and spice sector in the coming years.










